Delving into the details
What is Software?
Types of Software
System Software

Application Software
- Word Processors: Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Writer, Google Docs
- Presentation Software: Microsoft PowerPoint, LibreOffice Impress, Google Slides
- Web Browsers: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari
- Image Editing: Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, Paint.NET
- Accounting Software: QuickBooks, Sage, Wave
- Music: Spotify, iTunes, Deezer
- Video Games: Fortnite, League of Legends, Minecraft
Programming Languages: The Power to Create
- Java: A versatile language used for developing web, mobile, and desktop applications.
- Python: A simple and intuitive language, ideal for machine learning, data analysis, and web development.
- C++: A powerful and performant language, often used for creating video games, embedded systems, and critical applications.
Characteristics of Software
Broad Scope
Ubiquitous in our daily lives, software is characterized by its remarkable versatility, adapting to a multitude of tasks and activities. Whether you need to organize your schedule, edit photos, create presentations, or browse the internet, there’s dedicated software to simplify your life.
Installation Required
Beyond basic tasks, software ventures into increasingly sophisticated domains. It empowers scientists to model complex phenomena, engineers to design daring structures, and artists to push the boundaries of creativity. Its impact is felt across industries, from healthcare and education to manufacturing and commerce.
Independent Operation
Installation on a device is typically required to reap the benefits of software. This installation involves copying files, creating shortcuts, and configuring specific settings. Once installed, software operates independently, without the need for a constant internet connection. This advantage offers great flexibility and accessibility, allowing software use even in environments with limited or no internet connectivity.
What is an Application?
Types of Applications
Mobile Applications
Web Applications

Desktop Applications
Characteristics of Applications
A Specific Purpose
User-Friendly Interface
The Power of Connection
Regular Updates
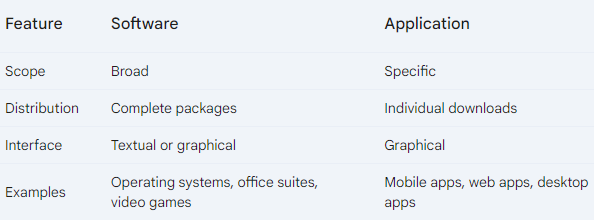
Key Differences Between Software and Applications